History of XR Technologies in Agriculture
Researchers first started considering ‘Virtual Agriculture’ (the use of Extended Reality (XR) technologies in the agriculture industry) as early as the year 2000 (Li, 2008). Virtual Agriculture encapsulates the concept of simulating agricultural processes through synergising Information Technology and Virtual Reality (VR) technology.
In the early 2000s, Virtual Agriculture was merely a concept since existing XR technologies such as the Sega VR-1 Motion Simulator (Williams, 2020) were simply not advanced enough to simulate agricultural processes neither in an accurate nor scalable way. However, this did not stop researchers from making future predictions on how XR technology might be used in agriculture.
For example, Li (2008) predicted that agricultural researchers would use VR technology to recreate real-world crop growing environment sandboxes as a tool to find more effective growing methods. He also predicted that VR would be used to teach regular people about agriculture through immersing them in a simulated agricultural environment and having them engage in farming activities.
Since Li’s analysis and predictions, XR technologies have advanced to the point of usability in the agriculture industry. Notable innovations that have enabled this include the Oculus Rift released in March 2013 (Lang, 2019) along with its following generations, the HTC Vive Focus 2 released in April 2016 (HTC, 2016) and the HoloLens 2 released in February 2019 (Forbes, 2019).
Technological advancements for XR content creation, such as the Insta360 Camera Sphere released in May 2022 (Insta360, 2022) used for 360 aerial drone shots and the game creation software Unity3D released in June 2005 (Unity, 2023), have also been responsible for enabling XR technologies to be properly used in agriculture.
Current State of XR Technologies in Agriculture
The current primary use cases for XR technologies in agriculture include education, marketing, and improving farming processes.
Agricultural Education and Marketing
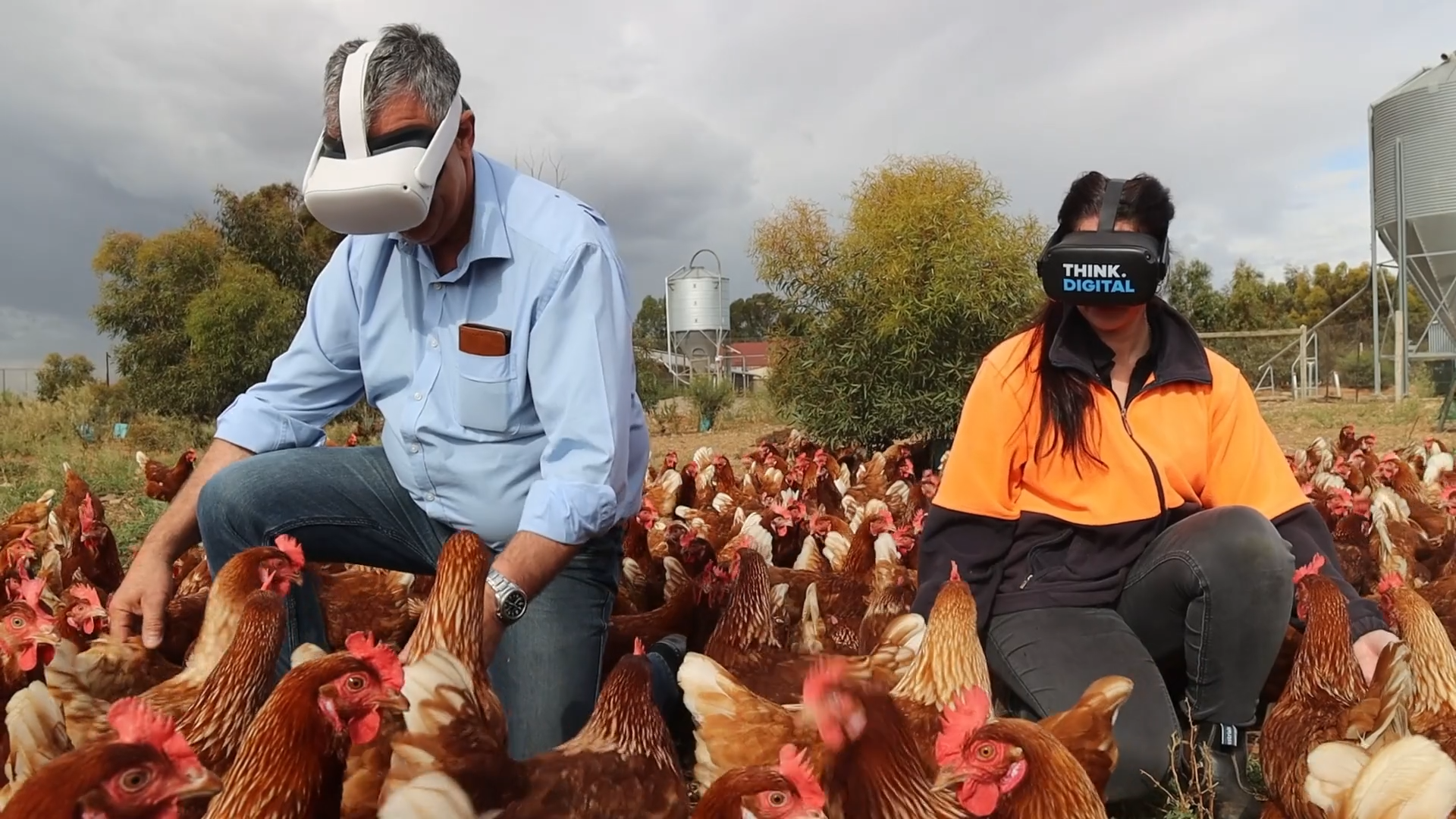
Immersive farm tours have been developed to be experienced in Virtual Reality. Think Digital Studios specialises in the creation of both 3DoF and 6DoF VR farm tours using 360 cameras, photographic enhancement software, and game creation software Unity3D (Staight, 2019) to produce these VR tours. The VR tours are compatible with headsets such as the Oculus Go and HTC Vive Focus 2 (Think Digital Studios, 2023).


Filming a ‘Farm Safety’ virtual tour (Think Digital Studios, 2023)
The virtual tours are used to educate both students and regular people on where their food comes from to encourage them to waste less food and make healthier dietary choices. The virtual tours are also used as an innovative marketing tool by farms to show off their facilities and advertise the authenticity of their produce. For instance, Think Digital Studios in collaboration with Woolworths have instigated the ‘Fresh Food Kids Discovery Tours’ program (Woolworths, 2023).
The flagship feature of this program is a Virtual Reality bus used as a mobile VR classroom fitted with Oculus Go headsets. The bus is driven to different locations around Australia to teach kids about where ‘Odd Bunch’ fruits and vegetables come from by engaging them in a virtual farm tour. This educational program also serves as a marketing tool for Woolworths, building consumer trust through educating the public on how the supermarket chain’s fruits and vegetables are sourced.
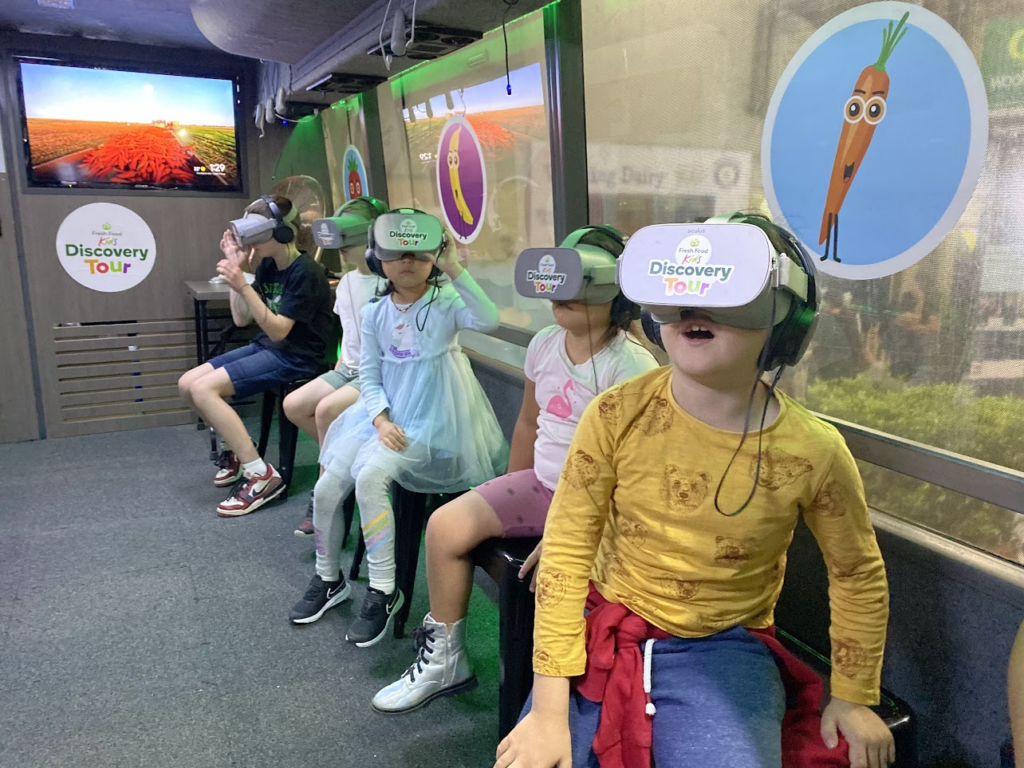


The Think Digital coach travels Australia to provide agriculture education using XR
XR technologies are recently being utilised in school-based agricultural education (Wells & Miller, 2020). For example, the immersive technology company Lumination has produced a curriculum-aligned program that educates teachers on how to teach students about using XR technologies to innovate sustainable farming systems. The program involves practical learning through having students digitally design and program sustainable farms that can be simulated and experienced in 3DoF VR headsets such as the Homido Prime (Lumination, 2023).
Improving Farming Processes
XR technologies are currently being used to effectively train and upskill farmers. In 2020, game development studio Novus Res in collaboration with the Australian Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment developed an interactive Virtual Reality simulation to train farmers on how to prevent and deal with Foot and Mouth Disease (Wilson & Wilson, 2020). The simulation teaches farmers strategies such as how to thoroughly inspect animals for diseases, how to set up a biosecurity control point, and how to appropriately interview agricultural landowners.


FMD Virtual Reality training (Wilson & Wilson, 2020)
Some VR training simulations can even facilitate multiple trainees and educators to interact with each other in real time. Think Digital Studios has developed a Metaverse-powered multiplayer framework that employers can use to train staff (Think Digital Studios, 2022). For example, one of their clients, the Australian Meat Processors Corporation, uses this framework to train employees in meat processing. The training process works efficiently even if the trainee is based in a totally separate real-world location to the educator.
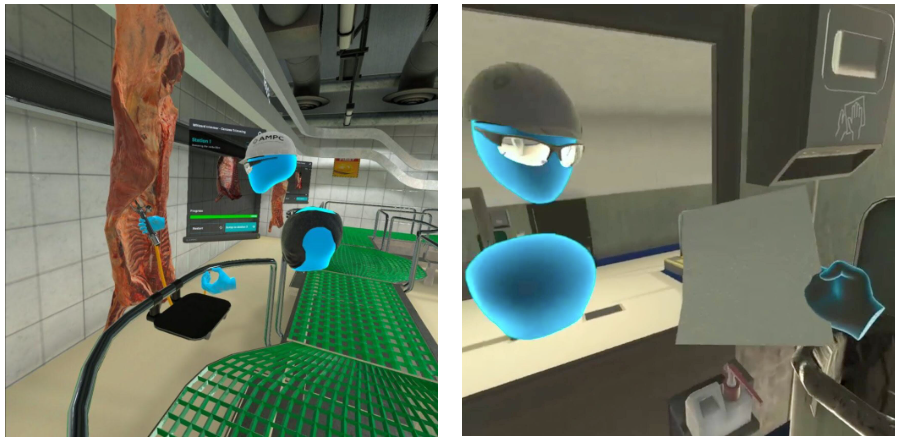
Metaverse-powered VR meat processing employee training (Think Digital Studios, 2022)
There are companies experimenting with integrating XR technologies in their farms to improve crop growing processes. Agricultural technology startup Plant Vision has built a prototype farm that integrates Mixed Reality (MR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies as its main system for crop management (Plant Vision, 2023).
Workers wear MR glasses that can instantaneously provide them with crucial maintenance details for each individual plant. For example, by simply looking at a particular tomato plant, a worker can find out exactly how long until it needs to be watered or picked. A worker can also scan a plant with their smartphone to find out how healthy it is and what can be done to improve the plant’s wellbeing. Through gamifying crop maintenance processes, Plant Vision enables higher efficiency and approval from workers who use the system (Oprescu et al., 2014).


MR being used for plant management (Plant Vision, 2023)
Current Fulfilment of Past Agricultural XR Technology Predictions
As predicted by Li (2008), Virtual Reality is currently being used to teach regular people about agriculture through immersing them in a simulated agricultural environment and having them engage in farming activities.
Companies such as Think Digital Studios have exceeded this prediction by enabling professional agricultural training. Li’s other prediction that information technology and Virtual Reality technology would be used to recreate real-world crop growing environment sandboxes as a tool to find more effective growing methods has not been fully fulfilled. Information technology software that simulates crop growing processes with scientific accuracy does exist (Yu, 2009). However, there is not yet evidence that this exists in a VR capacity.
Predictions for XR Technologies in Agriculture – Next 10 Years
Based upon the exponentially improving trajectory of XR technology advancement in agriculture, achievements over the next decade have been predicted:
- Li’s prediction will be completely fulfilled and scientifically accurate crop growing simulators will exist in a Virtual Reality capacity. This will be considered an upgrade from information technology simulators since researchers will be able to experiment and learn more efficiently due to experiencing embodiment and presence.
- Building upon existing multiplayer frameworks for agricultural training, it will become mainstream for farmers to remotely market crops, tools and animals through virtual shows and auctions hosted in either Virtual Reality or Mixed Reality. This will encourage affluent trade and, as such, will rapidly strengthen the agricultural industry’s economy.
- Building upon a system such as Plant Vision, Mixed Reality and Augmented Reality crop maintenance systems will be scaled up to facilitate use in full scale outdoor farms. These XR systems will also have the ability to analyse individual animals. This will greatly improve productivity and product quality on farms that implement the system.
References
Scholarly Articles
Li, H. (2008). Analysis of virtual reality technology applications in agriculture. In Computer And Computing Technologies In Agriculture, Volume I: First IFIP TC 12 International Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture (CCTA 2007), Wuyishan, China, August 18-20, 2007 1 (pp. 133-139). Springer US.
Oprescu, F., Jones, C. and Katsikitis, M. (2014). I PLAY AT WORK—ten principles for transforming work processes through gamification. Frontiers in psychology, 5, p.14. Wells, T. and Miller, G. (2020). Teachers’ Opinions About Virtual Reality Technology in School-based Agricultural Education. Journal of Agricultural Education, 61(1), pp.92-109.
Yu, F. (2009) ‘The Research and Application of Virtual Reality (VR) Technology in Agriculture Science’, Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture III, 317, pp. 546–550.
Websites
Forbes (2019) Hololens 2: Microsoft’s enterprise AR Power Play for Windows Mixed Reality, Forbes. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/moorinsights/2019/04/08/hololens-2-microsofts-enterprise-ar-power-play-for-windows-mixed-reality/?sh=6b5e74ef7e71.
HTC (2016) HTC United States. Available at: https://www.htc.com/us/newsroom/2016-06-07/.
Insta360 (2022) Buy sphere – invisible drone 360 camera – insta360, Insta360 Store: The Official Store for Insta360 Cameras, Accessories and Services. Available at: https://store.insta360.com/product/sphere?c=1846&from=nav.
Lang, B. (2019) Oculus rift S revealed with inside-out tracking, Resolution Bump, & New Ergonomics, Road to VR. Available at: https://www.roadtovr.com/oculus-rift-s-specs-release-date-announcement-gdc-2019/.
Lumination (2023) The Future of Food: Lumination: Lesson Plan, Lumination. Available at: https://lumination.com.au/resources/the-future-of-food/.
Plant Vision (2023) Plant vision, Plant Vision. Available at: https://www.plantvision.org/.
Staight, K. (2019) Agriculture turns to virtual reality to boost big business and attract new blood, ABC News. Available at: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2019-03-02/vr-farming-takes-off-in-agribusiness/10851278.
Think Digital (2023) Virtual reality workshops & training, Think Digital. Available at: https://think.digital/what-we-do/virtual-reality-workshops-training/.
Unity (2023) Unity real-time development platform: 3D, 2D, VR & AR engine, Unity Real-Time Development Platform | 3D, 2D, VR & AR Engine. Available at: https://unity.com/.
Williams, K. (2020) The Virtual Arena – Blast from the past: The VR-1, VRFocus. Available at: https://web.archive.org/web/20200811132324/https://www.vrfocus.com/2020/07/the-virtual-arena-blast-from-the-past-the-vr-1/.
Woolworths (2023) Fresh Food Kids Discovery Tours, Woolworths. Available at: https://www.woolworths.com.au/shop/discover/fresh-food-kids/discoverytours.
Reports
Wilson and Wilson (2020) Virtual reality to support FMD training.


